SUTURE MATERIALS
Surgical
sutures
Ideal
suture should be:
- Easy to handle
- Have minimally
reaction in tissue
- Inhibits bacterial
growth
- Holds securely when
knotted
- Resist shrinking in
tissue
- Is noncapillary, nonallergenic, noncarcinogenic and
nonferromagnetic
- Absorbs with minimal
reaction after tissue has healed
NOTE: Such an ideal suture does not exist.
CHARACTERISTICS OF SUTURES
- Suture size
The smallest diameter suture that will adequately hold the mending
wounded tissue should be used in order to minimize trauma as the suture passed
through the tissue. And also to reduce the amount of foreign material left in
the wound. A suture should not be stronger than the sutured tissue.
The most commonly used standard for suture size is the USP (United
States Pharmacopoeia), which denotes dimension from 10-0 the smallest and 7 the
largest.
- Flexibility
The flexibility of suture is determined by its torsional stiffness and
diameter, which influence its handling and use.
- Surface characteristic
The surface characteristics of suture influence the ease with which is
pulled through tissues (i.e., the amount of friction or ″drag″) and
the amount of trauma caused.
- Capillarity
Capillarity is the process by which fluid and bacteria are carried into
the interstices of multifilament fibers. Capillary suture materials should not
be used in contaminated or infected sites. Coating reduces capillarity of some
sutures.
- Knot tensile strength
Knot tensile strength is measured by the force that suture strand can
withstand before it breaks when knotted.
- Relatively knot security
The knot-holding capacity of suture material is the strength required to
untie or break a defined knot by loading the part of the suture that forms the
loop.
Sutures material may be classified:
- According to their
origin:
a)
organic
b)
synthetic
c)
metallic
- According to their
behavior in tissue:
a)
absorbable
(phagocytized or hydrolyzed)
b)
nonabsorbable
- According to their
structure
a)
monofilament
► Monofilament vs. Multifilament ◄
Monofilament
sutures:
Monofilament
sutures are made of a single strand of material.
Advantage
- have less tissue drag
than multifilament suture,
- do not have
interstices that may harbor bacteria.
Disadvantage
o
with
thicker threads the wiriness that is a characteristic of all monofilament threads
impairs handling and in particular renders knot-tying more difficult,
o
care should be used in
handling because nicking or damaging them with forceps or needle holder weakens
them and predispose them to breakage.
Multifilament
suture
Multifilament
sutures are made of several strands of suture that are twisted or braided
together.
Advantage
- are more pliable and
flexible than monofilament sutures,
- results in considerably better knot holding security.
Disadvantage
- the longitudinal orientation of the individual filaments within the
thread results in relatively high capillarity, but the capillarity of
braided threads is less than that of twisted threads.
- have a rough surface that impairs passage through tissue.
Multifilament threads are
generally coated. The coating smoothes out the irregular surface and thus
facilitates passage through tissue without impairing knot-holding security.
Coated multifilament threads are less stiff and wiry than monofilament threads.
The coating also reduces capillarity.
►some
types of the suture materials (table 1) ◄
Surgical
needles
Surgical
needles are divided in two groups:
- Traumatic needles
- Atraumatic needles
Traumatic needles (picture
1) - are needles with holes or eyes which are supplied to the hospital separate
from their suture thread. In traumatic needles with eyes, the thread comes out
of the needle's hole on both sides. When passing through the tissues, this type
of suture rips the tissue to a certain extent, thus the name traumatic.
![]()

![]()
Picture 1. Traumatic needles
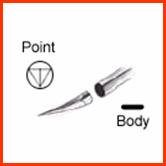
Atraumatic needles with
sutures (picture 2) -
comprise an eyeless needle attached to a specific length of suture thread.
Important thing is that the suture end of a swaged needle is smaller than the
needle body.
With attached suture thread

Picture 2. Atraumatic needle
Needles shapes:
- Straight skin, nervs, GI tract, tendons, blood vessels, etc.
- Halfcurved skin (rarely used one),
- Curved according to curve degree are divided:
- 1/4 circle eye,
microsurgery,
- 3/8 circle used for
the most body structures,
- 1/2 circle - used for
the most body structures,
- 5/8 circle urinary
and reproductive system.
- Combine needle anterior segment of the eye.

![]()
![]()
Straight needle Halfcurved neddle
Combine needle
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()


![]()
1/4
circle 3/8 circle 1/2 circle 5/8 circle
Point and body shape:
- Taper taper point and round or quadrangular body (cross section)
aponeurosis, muscles, nerves, peritoneum, blood vessels, valves.
- Blunt - blunt point and flat body (cross section) bowels, kidney, spleen,
liver.
- Triangular triangular point and flat or quadrangular body (cross section). If
the cutting side of triangular is upward this type of needle is called
conventional (skin, sternum), and if its downward reverse cutting (fascia, ligaments, skin, tendons).
- Tapercut - small triangular cutting point and flat body (cross section) fascia,
ligaments, uterus, oral cavity and etc.

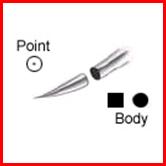
Taper
Blunt
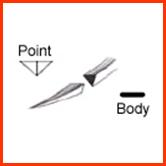
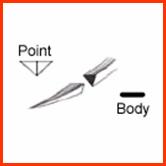
Conventional Reverse cutting
Tapercut
REFERENCES:
- http://www.ethicalagents.co.nz/pages/Apr%2005%205.htm
- Ethicon wound closure manual, Ethicon INC. a Johnson-Johnson
company